Herd immunity describes the point at which a population is immune enough to a disease to prevent it from circulating. In the current pandemic situation, why herd immunity is so important for mankind?.
Here we have explained the importance of herd immunity1 and how it will be useful in the prevention of coronavirus.
Definition of Herd Immunity
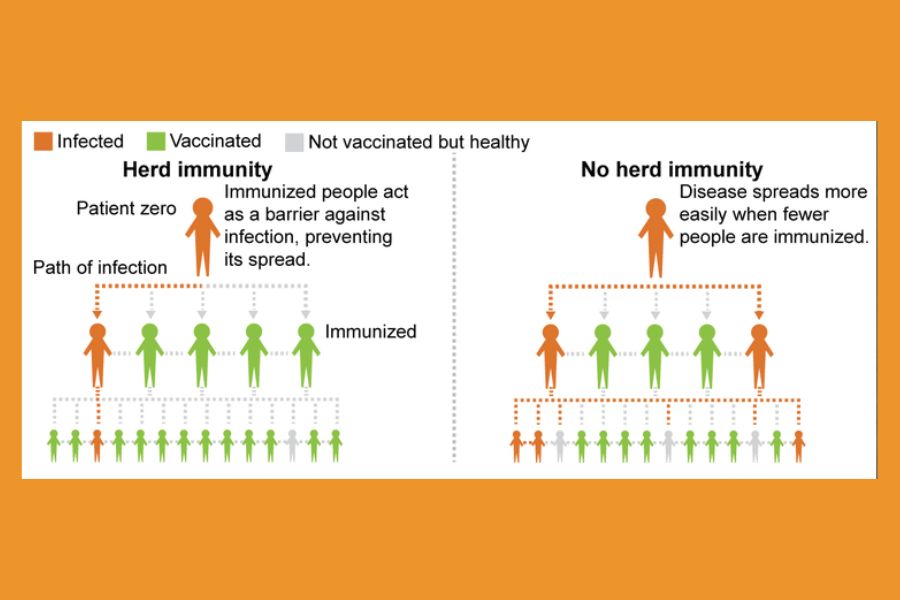
In simple form, Herd Immunity is defined as when the majority of the people or the herd get immune to an infectious disease, further spreading of the same infection in that community is unlikely. This means, that the whole community including the immune and not immune members are also gets protected.
Herd immunity percentage or the herd immunity threshold
For starting community spread of an infection, a percentage of people need to get an infection, this percentage is called threshold proportion, when the number/percentage of immune crowd number goes more than this threshold, a reduction in the infection spreading level can be found, this is called herd immunity threshold.
The percentage needed for herd immunity is about 40%, however, there are cases in which the same was gone beyond even 80%
The research and analysis were done by the Professor Frank Ball from the University of Nottingham2, has suggested that if approximate 43% of people get immune to Covid18, can help in getting herd immunity3
Why is herd immunity important?
Herd immunity is important because the members of the community who cannot be vaccinated like infants and children who are too young or immune-compromised patients can also be protected by it. For hampering the community spread of any major infection herd immunity is very important.
How can someone get herd immunity works in the body?
There are two ways one can get heard immunity. One is through vaccination and another one is through infection
Through vaccine herd immunity
Vaccines have a major role in herd immunity. We have controlled many life-threatening infections through this methodology. In the case of vaccines herd immunity, a Vaccine creates a situation that is similar to an infection, however, most of the time it does not cause any complication or illness. Vaccines actually signal the body to create immunity. Few of these can give lifelong immunity however, protection of some vaccines can get reduced or disappear over time. This can be further boosted by giving a booster dosage.
Acceptance of vaccination has increased from time to time, however in many developed and developing countries, there are communities who don’t accept vaccination, Many diseases like measles were resurged due to this situation. When there is reduced exposure to vaccination, there will be increasing in the spread of contagious diseases
Natural Herd immunity through infection
When a sufficient number of the community where recovers from a contagious infection, usually they have developed antibodies against further infection of the same pathogen.
When the H1N1 infection was spreading, it is found that those people who are infected in 1918 during the influenza pandemic were found later with immunity to the H1N1 infection during 2009-10.
But there is a different way to get herd immunity. If the pathogen in question induces lifelong immunity and can spread more or less unchecked, the rates of infections increase exponentially, so they eventually flatter, worsen and vanish, more people catch and recover without the introduction of a vaccine.
However, for two reasons, this method is much less reliable.
First, it only works within a relatively closed population in which new, unexposed individuals do not arrive constantly to provide hungry pathogens with fodder. Even isolated communities are not completely safe from this risk, since “children are not born with immunity,” Hunter said. “Many diseases that we would expect to die out due to herd immunity remain around because there are just enough newborns entering the population to keep the disease going.”
Second, herd immunity through acquired infection only takes hold if the disease is actually contracted by a sufficient proportion of the population. According to preliminary data from affected European countries and a report from Spain published in the journal The Lancet in July 2020, this is not a foregone conclusion and is almost definitely not the case with COVID-19. The numbers suggest that the novel coronavirus infected only a fraction of the population – far below the herd immunity threshold, despite dire losses.
Is COVID-19 capable of achieving herd immunity?
It is possible that with an appropriate vaccine we may achieve herd immunity and end the COVID-19 pandemic. But daily booster shots will probably be required, as early patient recovery results indicate that the novel coronavirus offers immunity for a few months or years only.
“We know that in patients with SARS, MERS, and seasonal coronavirus, two or three years after an infection, antibodies become undetectable so this is no surprise,” Poland said. “In this situation, the notion that I’ll get a vaccine and be completely immune in the way it did with measles, rubella, smallpox or polio is simply not real,” he said.
- Heart Age Calculator - August 12, 2025
- Home Workout Estimator - July 29, 2025
- Plant-Based Macro Calculator - July 29, 2025